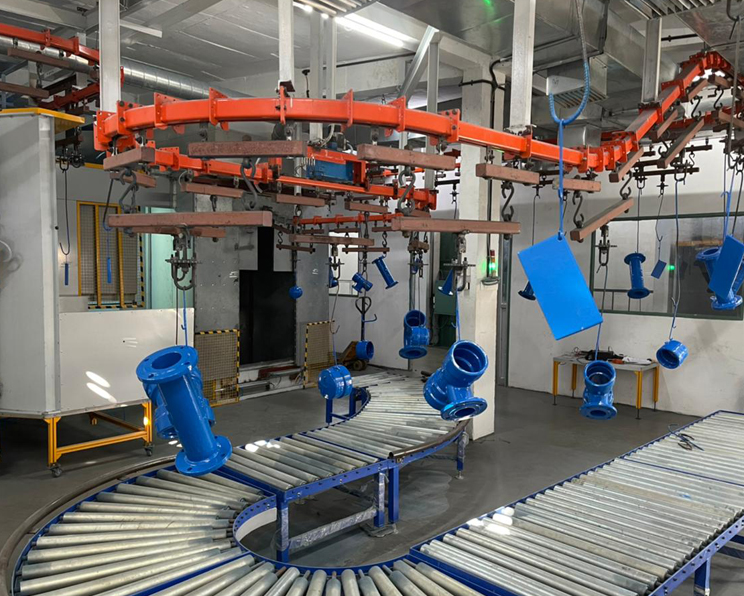
FBE Coating Process
The process of FBE coating comprises of essential components viz,
Resin
Hardener or curing agent
Fillers and extenders
Colour pigments
The resin and hardener part together is known as the "Binder". As the name indicates, in Fusion bonded epoxy coatings the resin part is an "epoxy" type resin. The most commonly used FBE resins are derivatives of biphenyl A and epichlorohydrin. However, other types of resins (for example biphenyl (F type) is also commonly used in FBE formulations to achieve various properties, combinations or additions. Resins are also available in various molecular lengths, to provide unique properties to the final coating.
The other part of FBE coatings is the curing agent or hardener. Curing agents react either with the epoxy ring or with the hydroxyl groups, along the epoxy molecular chain. With various types of curing agents used in FBEC process, the curing agent determines the nature of the final FBE product with its cross linking density, chemical resistance, brittleness, flexibility etc. The ratio of epoxy resins and curing agents in a formulation is determined by their relative equivalent weights.
Apart the above two major components, FBE coatings include fillers, pigments, extenders and various additives, to provide desired properties. These components control characteristics such as permeability, hardness, color, thickness, gouge resistance etc. All of these components are normally dry solids, even though small quantities of liquid additives may be used in some FBE formulations. If used, these liquid components are sprayed into the formulation mix during pre-blending in the manufacturing process.